What Is Cognitive AI? |Is It the Future?|How Is Cognitive Computer Different?
A cognitive computer or system interacts with people in a natural way, learns on a large scale, and uses intentional reasoning. These systems learn and reason via interactions with people and their experiences in their surroundings, as opposed to being deliberately coded. Artificial intelligence and cognitive computing have some overlap, and the technology used to power cognitive applications are comparable. We shall learn more about cognitive
How does cognitive computing work?
How Does Cognitive Computing Function?
AI vs. cognitive computing
Applications of Cognitive AI in Use Cases
How does cognitive computing work?

Cognitive computing is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that aims to simulate human thought processes and behavior in order to solve complex problems and make better decisions. It involves using advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to enable computers to process and understand vast amounts of data, learn from patterns, and reason like humans.
Here's a general overview of how cognitive computing works:
1.Data Collection: The first step in cognitive computing is gathering relevant data from various sources, such as text, images, audio, and video. This data can be structured or unstructured, and it may come from databases, the internet, sensors, or other data repositories.
2.Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is a crucial component of cognitive computing. It allows the computer to understand and interpret human language in a way that enables it to comprehend written or spoken inputs. This is essential for interactions with users and for extracting valuable insights from textual data.
3.Machine Learning: Cognitive computing heavily relies on machine learning algorithms. These algorithms allow the system to identify patterns, relationships, and trends within the data. By learning from historical data, the system can make predictions and inferences about new, unseen data.
How Does Cognitive Computing Function?
Cognitive computing functions by combining several key technologies and techniques to mimic human cognitive abilities, such as understanding language, reasoning, learning, and problem-solving. Below are the main components and functionalities that enable cognitive computing to work:
1.Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It involves tasks like speech recognition, language understanding, and language generation. NLP allows cognitive computing systems to interact with users through natural language interfaces and process unstructured textual data.
2.Machine Learning: Machine learning is a crucial aspect of cognitive computing. It involves the use of algorithms that enable computers to learn from data, identify patterns, and make predictions without explicit programming. Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning are common techniques used in cognitive computing to analyze data and learn from it.
3.Knowledge Representation: Cognitive computing systems need to represent knowledge in a structured and organized manner. This involves creating models, graphs, ontologies, or other forms of knowledge representation that allow the system to reason and infer connections between different pieces of information.
4.Reasoning and Problem Solving: Cognitive computing systems apply reasoning techniques to draw conclusions and make decisions based on the information they have processed and learned from. Reasoning mechanisms may include deductive, inductive, abductive, or probabilistic reasoning.
5.Context Awareness: Understanding context is critical for cognitive computing systems. They consider the broader context in which data is presented, user preferences, historical data, and other relevant factors to provide more accurate and relevant responses and recommendations.
- AI vs. cognitive computing
- The technology underlying cognitive computing and artificial intelligence are related. These consist of NLP, neural networks, machine learning, deep learning, and more. They do, however, also differ in a number of ways.
- These were a few of the distinctions between the two, thus. Let's proceed and use an example to better comprehend the concept of cognitive AI.
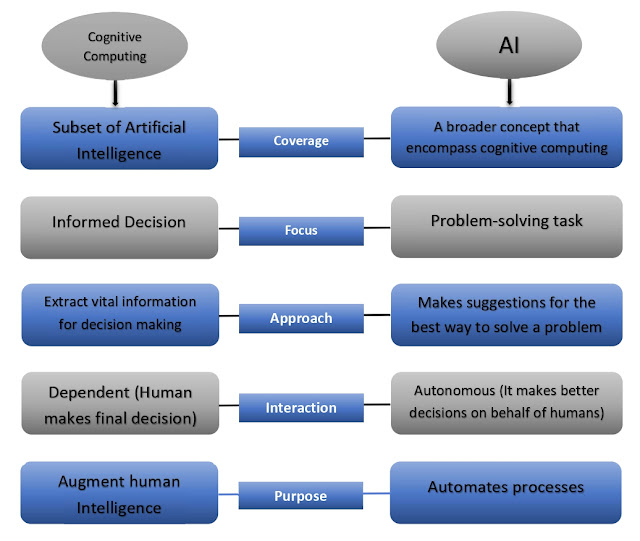
AI (Artificial Intelligence) and cognitive computing are related but distinct concepts. AI is a broader field that encompasses various technologies and approaches aimed at creating intelligent systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. On the other hand, cognitive computing is a specific subset of AI focused on simulating human thought processes and decision-making.
Here are the key differences between AI and cognitive computing:
Scope:
- AI: Artificial Intelligence covers a wide range of techniques and applications that aim to create machines capable of performing tasks that usually require human intelligence. This includes tasks like speech recognition, image understanding, natural language processing, robotics, game playing, and more.
- Cognitive Computing:
- Cognitive computing is a specialized branch of AI that specifically focuses on emulating human cognitive abilities, such as understanding language, reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
Approach:
- AI: AI employs various methods, including rule-based systems, machine learning, neural networks, expert systems, and statistical algorithms, to create intelligent systems.
- Cognitive Computing: Cognitive computing relies heavily on advanced machine learning techniques and natural language processing to understand and process vast amounts of unstructured data and simulate human thought processes
Goal:
- AI: The ultimate goal of AI is to create intelligent machines that can perform tasks as effectively or better than humans, across a wide range of domains.
- Cognitive Computing: The main goal of cognitive computing is to create systems that can understand and interact with humans in a more natural and intuitive manner, making use of advanced reasoning and learning capabilities.
Human Interaction:
- AI: AI systems may or may not interact directly with humans. Many AI applications function in the background, optimizing processes or providing recommendations without direct human interaction.
- Cognitive Computing: Cognitive computing is designed to have more natural and seamless interactions with humans. It focuses on understanding natural language, providing personalized responses, and reasoning like humans.Decision Making:
- AI: AI systems can make decisions based on predefined rules or learned patterns from data, but they may not necessarily simulate human-like reasoning.
- Cognitive Computing: Cognitive computing systems attempt to mimic human reasoning and decision-making processes, often incorporating probabilistic or fuzzy logic approaches to handle uncertainty and incomplete information.
- In summary, AI is a broader field that encompasses various technologies aimed at creating intelligent systems, while cognitive computing is a specific subfield of AI that concentrates on simulating human cognitive abilities and providing more human-like interactions and decision-making capabilities.
- Applications of Cognitive AI in Use Cases
Cognitive AI has numerous applications across various industries and use cases due to its ability to simulate human-like thinking and understanding. Here are some common applications of cognitive AI in different domains:
- Customer Service: Cognitive AI can be used in chatbots and virtual assistants to provide personalized and intelligent customer support. It can understand natural language queries, offer relevant responses, and handle customer inquiries efficiently, improving the overall customer experience.
Healthcare Diagnosis: In healthcare, cognitive AI can assist medical professionals in diagnosing diseases and suggesting treatment plans. By analyzing patient data, medical records, and research literature, cognitive AI systems can provide valuable insights to support clinical decision-making.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Cognitive AI is extensively used in NLP applications, such as sentiment analysis, language translation, speech recognition, and text summarization. These capabilities enable better understanding and processing of human language.
Fraud Detection: Cognitive AI can be employed in financial institutions to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. It can analyze transaction patterns, identify anomalies, and flag suspicious transactions in real-time, helping to minimize financial losses.
Personalized Recommendations: Cognitive AI is utilized by recommendation systems in e-commerce, content streaming platforms, and social media to offer personalized product or content recommendations based on user preferences, behavior, and historical data.
Autonomous Vehicles: In the automotive industry, cognitive AI is used in autonomous vehicles to perceive and understand the environment, make real-time decisions, and navigate safely through complex traffic scenarios.
- These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of cognitive AI across different industries. As the technology advances, more innovative use cases are likely to emerge, further enhancing efficiency and decision-making in various domains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
Q1: How is Cognitive AI used in customer service? A1: Cognitive AI is employed in chatbots and virtual assistants to provide intelligent and personalized customer support. These systems can understand natural language queries, offer relevant responses, and handle customer inquiries efficiently.
Q2: Can Cognitive AI assist in healthcare diagnosis?
A2: Yes, Cognitive AI can analyze patient data and medical records to assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing diseases and suggesting treatment plans, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Q3: What industries can benefit from Cognitive AI? A3: Cognitive AI has applications across various industries, including healthcare, finance, education, automotive, manufacturing, and customer service, among others.
Q4: How does Cognitive AI contribute to autonomous vehicles? A4: In autonomous vehicles, Cognitive AI enables perception of the environment, real-time decision-making, and safe navigation through complex traffic scenarios, ensuring the safety and efficiency of self-driving cars.
Conclusion: Cognitive AI represents a paradigm shift in the realm of Artificial Intelligence, bringing us closer to intelligent systems that can think and reason like humans. With its potential to revolutionize industries, enhance user experiences, and enable personalized decision-making, Cognitive AI undoubtedly holds a promising future as a key driving force in the ever-evolving world of AI.











.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


0 comments:
Post a Comment